How Agentic AI and Human-in-the-Loop Collaboration are Redefining Commerce
September 22, 2025

Samesurf invented modern co-browsing.
The e-commerce landscape is on the brink of a profound transformation. The industry is now moving beyond reactive tools and simple recommendations to an era of “agentic commerce,” where AI systems act autonomously on behalf of users. This summary provides a strategic analysis of this shift, delineating the fundamental differences between Agentic AI and its predecessors. It outlines a four-level progression of autonomous shopping, from basic search to full purchasing delegation.
While this evolution promises unprecedented efficiency and personalization, it introduces a critical “trust paradox”—a psychological and practical barrier to consumer adoption, particularly for high-value or emotionally resonant purchases. This report is based on the premise that a purely autonomous model is not the most viable path to scalable success. Instead, the optimal strategy lies in a hybrid, human-in-the-loop framework where Agentic AI handles high-volume, low-stakes tasks, and a human expert intervenes for complex, trust-sensitive interactions. Finally, this report demonstrates how Samesurf’s patented technology serves as the essential bridge for this hybrid model, transforming moments of potential frustration into opportunities for trust-building, visual collaboration, and increased conversion.
The Agentic AI Revolution—Beyond Generative AI
The ongoing evolution of artificial intelligence is fundamentally re-engineering how digital services are provided, with Agentic AI emerging as the next significant leap forward. To grasp its transformative potential, it is essential to first establish a clear, foundational understanding of what Agentic AI is and how it distinguishes itself from previous generations of AI technology. This shift represents a move from systems that merely respond to commands to those that proactively take action.
Defining the Autonomous Core: Autonomy, Reasoning, and Action
Agentic AI represents an advanced class of artificial intelligence characterized by its capacity for autonomous decision-making and action. Unlike traditional AI systems which are typically reactive and operate within rigid, predefined frameworks, agentic AI can set goals, plan, and execute tasks with minimal human intervention. These independent systems are designed to automatically respond to dynamic conditions by taking procedural, algorithmic, and even creative steps to produce a desired outcome.
The power of Agentic AI is rooted in a set of mutually reinforcing design principles with Large Language Models (LLMs) serving as a central “brain” for reasoning. This reasoning capability allows an agent to analyze gathered data, understand context, and formulate potential solutions. A key component of this process is goal decomposition, where a complex, high-level goal is broken down into smaller, more manageable sub-tasks. For example, a user’s request to an AI enabled device to “plan a trip” is not handled as a single, static prompt; rather, the agent will decompose it into a series of actionable steps, such as “book flights,” “find hotels,” and “plan an itinerary”. Critically, these agents are not self-contained; they utilize a variety of tools and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to gather real-time data and execute actions within underlying systems to achieve their objectives. This enables them to go beyond content creation or simple function calling and effectuate real-world changes.
The Three-Tiered AI Landscape: A Framework for E-commerce
To better understand the place of Agentic AI in the broader technological ecosystem, a three-tiered framework helps to delineate the landscape:
- Tier 1: Traditional AI and Chatbots: These systems are at the base of the pyramid. They are reactive since they operate on scripted responses and rigid decision trees. A traditional chatbot might be able to answer a “yes” or “no” question about product stock or provide a pre-programmed response to a frequently asked question, but their functionality is limited to their programming.
- Tier 2: Generative AI: This tier is focused on the creation of new content based on user prompts, such as text, images, or code. An LLM is at the heart of this technology, and its primary value is derived from what the model can generate. In an e-commerce context, a generative AI model could be used to create marketing copy or suggest product ideas, but it does not take autonomous action.
- Tier 3: Agentic AI: Sitting at the top of the pyramid, Agentic AI is a subset of generative AI that is centered around the orchestration and execution of agents. It utilizes an LLM as its “brain” to perform actions through tools, but its primary function is to go beyond content creation to achieve higher-level goals. For instance, a generative AI model might create marketing materials, but an Agentic AI system could then be used to deploy those materials, track their performance, and automatically adjust the strategy based on the results, without further human input.
The fundamental difference across these tiers is the shift from a passive response to a proactive action. While an AI agent might perform a specific task, Agentic AI is the overarching system that coordinates and manages multiple agents to handle complex, multi-step workflows. The progression to Agentic AI marks a fundamental shift from a “creation-based” to an “orchestration-based” economy for digital services. The efficiency gains from generative AI content creation have created a new operational bottleneck: how to deploy and manage this vast amount of content at scale. Agentic AI emerges to solve this problem by taking on the execution layer, transforming AI from a creative assistant into a proactive virtual collaborator. This signifies that the focus of technology investment is shifting from building better models to building more effective orchestration layers that can manage and deploy those models to achieve complex, real-world objectives.
The Emergence of Autonomous Shopping
The retail industry is on the brink of its next seismic shift, driven by the emergence of Agentic AI and the concept of “agentic commerce”. This new paradigm is fundamentally re-engineering how shoppers discover, decide, and buy, moving beyond traditional search queries to a world where intelligent agents proactively manage the entire shopping journey.
From Assisted to Autonomous: A New Customer Journey
The old e-commerce model relied on customers manually researching and transacting themselves. The new model, driven by agentic AI, is proactive and self-directed. Instead of a customer using a chatbot to ask for product ideas, the agent takes action on their behalf—from identifying a need, to comparing options, and finally completing a purchase. These agents are not just simple assistants; they are sophisticated systems capable of understanding complex requirements, comparing options, negotiating terms, and completing purchases. They can analyze market data, customer behavior, and financial statements to automate a wide range of tasks, from fraud detection to optimizing investment strategies. The core of their capability is the ability to go beyond simple keyword matching and use contextual information to provide highly relevant and personalized results, anticipating customer needs before they are even explicitly stated.
A Blueprint for Automation: The Four Levels of Agentic Commerce
To help leaders navigate this strategic shift, a four-level model of agentic commerce provides a clear blueprint for the progression of autonomous shopping.
- Level 1: Discovery and Research: At this initial stage, shoppers lean on generative AI platforms like ChatGPT or Gemini for brainstorming ideas, such as gift suggestions or workout gear. This is a low-friction, high-curiosity space where the primary opportunity for brands is to influence the user before a purchasing intent is solidified. The associated risk is that a brand’s unique storytelling may be replaced by generic AI suggestions unless its content is compelling and accessible.
- Level 2: Intelligent Find and Compare: The AI system provides curated search results that include product specifications, reviews, pricing, and retailer availability. For shoppers, this provides clarity and confidence in their decision-making. However, brands that lack structured product data or API accessibility may simply not appear in the results, as the agent’s ability to find and present information is dependent on the quality of the underlying data.
- Level 3: Seamless Buy and Execute: At this level, agents go beyond suggestions and actually complete the purchase. With access to a digital wallet and shipping preferences, the transaction is completed inside the agent’s own interface, eliminating the need for the user to navigate different websites or fill out forms. This reduces friction and is exemplified by systems like Amazon’s “Buy for Me”.
- Level 4: Autonomous Agentic Commerce: This is the final and most advanced stage. The agent proactively anticipates a user’s needs and purchases items based on data patterns and preferences, without any user request. This provides the ultimate convenience, as the user barely has to lift a finger. However, this level also introduces the most significant strategic risk for retailers.
The progression to Level 4 Agentic Commerce presents a fundamental threat of disintermediation to brands and retailers. In traditional e-commerce, the value chain is built on driving direct traffic to a brand’s website to facilitate the transaction. As commerce evolves to Level 3 and 4, the transaction is increasingly handled within the agent’s experience, bypassing traditional storefront browsing and creating a new competitive landscape. The brand-customer relationship becomes intermediated by the AI layer, and the source of customer loyalty shifts from the brand to the agent itself. The consequence is that brands must transition from traditional SEO to a new paradigm of “metadata marketing,” ensuring their product data is structured, complete, and accessible to agents to remain visible and competitive.
The Trust Paradox—Bridging the Gap Between Autonomy and Assurance
While the promise of Agentic AI is the ultimate in efficiency and convenience, the progression to a fully autonomous shopping experience is not without its friction. A significant psychological and practical barrier—a “trust paradox”—emerges as a key limiting factor to mass adoption, particularly for complex or emotionally resonant purchases.
Why Consumers Hesitate: The Trust-Autonomy Disconnect
The consumer’s willingness to delegate tasks to an AI agent varies dramatically based on the purchase category. For low-stakes, routine, and repetitive buys, such as replenishing laundry detergent, pet food, or coffee pods, automation is a welcome time-saver. The functional criteria are clear (availability, price, delivery time), and the trade-off of control for convenience is a straightforward benefit.
However, the dynamics shift entirely for high-stakes, emotional, or personal purchases, such as fashion, furniture, jewelry, or booking travel. In these scenarios, consumers are far more reluctant to give up control. Such decisions are not purely logical; they involve personal taste, mood, aspirations, and an emotional connection with the product. The complete removal of human interaction creates a critical “trust gap” that limits the application and scalability of a purely autonomous model. The core consumer concerns are explicit and actionable. Consumers worry about the security of their payment and personal data, the privacy of their personal information, the risk of the AI “misunderstanding needs,” and the potential for the AI to fail to recognize or prevent fraudulent activity.
The Case for a Hybrid Customer Journey
The flaw in a model of pure automation is that while it promises ultimate efficiency, it can also erode the very confidence required to complete a sale, especially in moments that require empathy and reassurance. The central challenge is a causal loop that will prevent the mass adoption of fully autonomous shopping. The more complex or high-value a task becomes, the more the consumer’s need for human assurance and control clashes with the agent’s core principle of autonomy. This creates a point of psychological friction. The agent’s independence, a benefit for routine buys, becomes a source of anxiety for emotional ones, because the consumer’s desire for control directly contradicts the AI’s core functionality.
For agentic commerce to scale beyond low-stakes use cases, the most viable path forward is a “human-in-the-loop” model. This approach leverages Agentic AI for its strengths—automating routine tasks and scaling efficiently—and strategically introduces a human expert to handle situations that require empathy, reassurance, or complex guidance. As one expert notes, the future of customer experience is a combination of “AI combined with human agents”. The most successful systems will be designed with a built-in “hand-off” mechanism to a human expert at these critical junctures, acknowledging that the trust gap is a feature of the current system – not a bug to be solved by further automation.
Samesurf’s Role in a Hybrid E-commerce Future
The strategic solution to the trust paradox lies not in more advanced AI, but in a seamless mechanism that can reintroduce human connection at the precise moments when it is most needed. Samesurf’s cloud browser and HITL technologies serves as the essential tool for effectuating this hybrid model, bridging the trust gap and converting high-stakes, agent-guided interactions into successful, human-assisted transactions.
The Power of a Shared Experience: What is Co-Browsing?
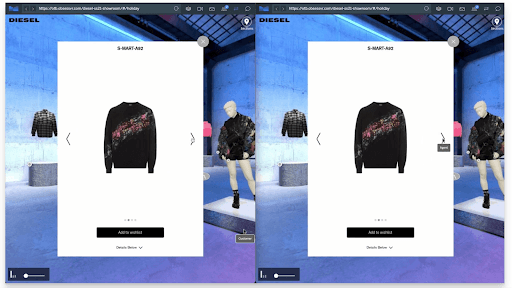
Samesurf is widely considered the inventor of modern co-browsing, a technology that allows multiple AI enabled and human user devices to experience the same web content in real time from any device, without the need for downloads or coding.
Samesurf’s core features are designed specifically to build trust and enhance collaboration. It instantly makes the customer “visible” to the agent by allowing the agent to see exactly what the customer sees on their webpage. This shared visual context reduces anxiety, helps customers feel “seen,” and significantly reduces the stress and uncertainty that often accompany complex online interactions. A human or AI enabled agent can use features like cursor tracking, screen drawing, and in-page control passing to provide real-time, visual guidance, walking the customer through complex forms or product pages. This visual guidance eliminates the frustration of back-and-forth communication and provides a clear path forward, much like a knowledgeable sales associate in a physical store. Furthermore, Samesurf’s security features are paramount; it uses TLS/SSL encryption and, crucially, provides data redaction that can automatically hide sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, in real time, ensuring privacy and compliance.
Samesurf as the Agent’s Human-Assisted Fail-Safe
Samesurf is not just a support tool; it is a strategic architectural component of the hybrid agentic commerce ecosystem. Among other components, it provides the crucial “human-in-the-loop” fail-safe that enables the scalability of agentic commerce beyond low-stakes use cases. When an Agentic AI bot encounters a high-friction moment—such as a complex checkout form, a high-value purchase, or a customer expressing hesitation—it can be configured to seamlessly hand off the interaction to a human agent.
This handoff mechanism transforms a potential point of friction into a moment of trust. A human agent can use Samesurf to instantly join the customer on the exact page they are on, providing live, visual guidance. For example, if a customer is comparing two products and has a complex question about specifications, a human or AI enabled agent can use a virtual pointer to highlight the relevant details or navigate to a comparison chart on another page. This direct, visual connection converts a potential abandoned cart into a confident purchase by addressing last-minute concerns and troubleshooting technical glitches with real-time assistance. This capability proves that Agentic AI’s weakness—its inability to instill trust or handle emotional decisions—is not an insurmountable problem. It simply creates a need for a seamless handoff mechanism, which Samesurf provides, ensuring the AI can recognize when its autonomy may be a liability and pivot to a human touchpoint.
Realizing the Hybrid Advantage
This hybrid approach allows businesses to leverage the speed and scalability of Agentic AI for the 80% of routine interactions while preserving the human connection that is essential for the 20% of high-value or trust-sensitive moments. This synergy boosts both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. By addressing customer concerns and troubleshooting technical issues with real-time visual assistance, Samesurf directly impacts the bottom line, significantly increasing the likelihood of a sale. This personalized approach demonstrates that the business is invested in the customer’s success, which fosters trust and builds stronger, more resilient customer relationships. The trust gap creates a need for a seamless “handoff” mechanism, and Samesurf’s technology provides the technical means to effectuate this handoff without friction. By transforming a frustrating, non-visual interaction into a shared visual experience with either a human or a complex AI enabled user, Samesurf closes the trust gap, converting the potential abandoned cart into a successful sale.
Navigating the Future of Agentic Commerce
The future of e-commerce is not a binary choice between human and AI, but a sophisticated, hybrid model that strategically leverages the strengths of both. Agentic AI offers an unprecedented opportunity for businesses to automate and scale operations, delivering efficiency and hyper-personalization for low-stakes, routine transactions. However, this technology introduces a fundamental challenge in its inability to build and sustain the level of trust required for high-stakes, emotionally resonant purchases. The complete removal of human interaction at these critical junctures creates a trust paradox that will prevent the mass adoption of a purely autonomous shopping experience.
The most viable path to scalable, profitable, and customer-centric agentic commerce is through a human-in-the-loop framework. This model acknowledges that the trust gap is a key point of friction and that the most effective systems will be those that can seamlessly recognize when their autonomy is a liability and pivot to a human touchpoint. Technologies like Samesurf’s synchronized browsing and Agentic AI solutions are not just support tools; they are strategic architectural components that provide the crucial bridge for this hybrid ecosystem. By transforming moments of friction into opportunities for visual collaboration and human connection, they enable businesses to harness the power of Agentic AI for efficiency while simultaneously fostering the trust and confidence that are essential for converting complex, high-value sales.
Based on this analysis, the following actionable recommendations are offered for key stakeholders:
- For Retailers: Invest in a hybrid strategy that integrates Agentic AI for low-stakes, high-volume tasks and a visual collaboration platform for high-stakes, trust-sensitive interactions. This approach will allow for operational scalability without sacrificing the customer trust that is essential for loyalty and brand resilience.
- For Technology Providers: Focus on building a modular, vendor-neutral architecture that enables seamless handoffs between agents and humans. The future of the industry is in platforms that can orchestrate a symphony of autonomous and human-assisted services.
For Marketers: Shift from traditional SEO to “metadata marketing” and ensure that all product data is structured and “agent-readable” through comprehensive APIs and rich metadata. Remaining visible in the new “agent-first” landscape will depend on the ability of AI agents to find, understand, and present a brand’s products to customers.
Visit samesurf.com to learn more or go to https://www.samesurf.com/request-demo to request a demo today.